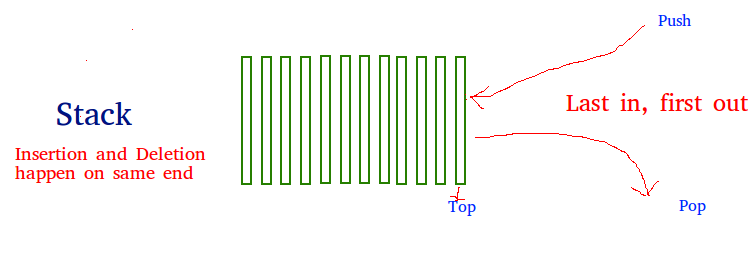
Stack¶
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out).
Basic Operations on Stack¶
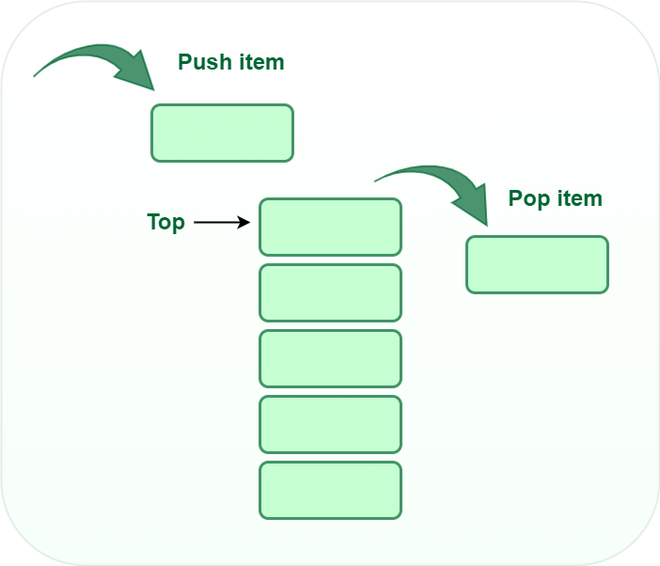
push(): to insert an element into the stackpop(): to remove an element from the stacktop(): Returns the top element of the stack.isEmpty(): returns true is stack is empty else false.size(): returns the size of stack.
| Operations | Complexity |
|---|---|
| push() | O(1) |
| pop() | O(1) |
| isEmpty() | O(1) |
| size() | O(1) |
Types of Stacks¶
- Register Stack: This type of stack is also a memory element present in the memory unit and can handle a small amount of data only. The height of the register stack is always limited as the size of the register stack is very small compared to the memory.
- Memory Stack: This type of stack can handle a large amount of memory data. The height of the memory stack is flexible as it occupies a large amount of memory data.
Applications of Stacks¶
- Redo-undo features at many places like editors, photoshop.
- Forward and backward features in web browsers
- Used in many algorithms like Tower of Hanoi, tree traversals, stock span problems, and histogram problems.
- In Memory management, any modern computer uses a stack as the primary management for a running purpose. Each program that is running in a computer system has its own memory allocations
- String reversal is also another application of stack. Here one by one each character gets inserted into the stack. So the first character of the string is on the bottom of the stack and the last element of a string is on the top of the stack. After Performing the pop operations on the stack we get a string in reverse order.
- Stack also helps in implementing function call in computers. The last called function is always completed first.
Implementation of Stack¶
There are two ways to implement a stack
- Using array
- Using linked list
# Python program for implementation of stack
# import maxsize from sys module
# Used to return -infinite when stack is empty
from sys import maxsize
# Function to create a stack. It initializes size of stack as 0
def createStack():
stack = []
return stack
# Stack is empty when stack size is 0
def isEmpty(stack):
return len(stack) == 0
# Function to add an item to stack. It increases size by 1
def push(stack, item):
stack.append(item)
print(item + " pushed to stack ")
# Function to remove an item from stack. It decreases size by 1
def pop(stack):
if (isEmpty(stack)):
return str(-maxsize -1) # return minus infinite
return stack.pop()
# Function to return the top from stack without removing it
def peek(stack):
if (isEmpty(stack)):
return str(-maxsize -1) # return minus infinite
return stack[len(stack) - 1]
# Driver program to test above functions
stack = createStack()
push(stack, str(10))
push(stack, str(20))
push(stack, str(30))
print(pop(stack) + " popped from stack")
# Python program for linked list implementation of stack
# Class to represent a node
class StackNode:
# Constructor to initialize a node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
# Constructor to initialize the root of linked list
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def isEmpty(self):
return True if self.root is None else False
def push(self, data):
newNode = StackNode(data)
newNode.next = self.root
self.root = newNode
print ("% d pushed to stack" % (data))
def pop(self):
if (self.isEmpty()):
return float("-inf")
temp = self.root
self.root = self.root.next
popped = temp.data
return popped
def peek(self):
if self.isEmpty():
return float("-inf")
return self.root.data
# Driver code
stack = Stack()
stack.push(10)
stack.push(20)
stack.push(30)
print("% d popped from stack" % (stack.pop()))
print("Top element is % d " % (stack.peek()))
Advantages of Stack¶
- Stack helps in managing data that follows the LIFO technique.
- Stacks are be used for systematic Memory Management.
- It is used in many virtual machines like JVM.
- When a function is called, the local variables and other function parameters are stored in the stack and automatically destroyed once returned from the function. Hence, efficient function management.
- Stacks are more secure and reliable as they do not get corrupted easily.
- Stack allows control over memory allocation and deallocation.
- Stack cleans up the objects automatically.
Disadvantages of Stack¶
- Stack memory is of limited size.
- The total of size of the stack must be defined before.
- If too many objects are created then it can lead to stack overflow.
- Random accessing is not possible in stack.
- If the stack falls outside the memory it can lead to abnormal termination.
Queue¶
A queue is a linear data structure that is open at both ends and the operations are performed in First In First Out (FIFO) order.
Basic Operations for Queue¶
Enqueue(): Adds (or stores) an element to the end of the queue..Dequeue(): Removal of elements from the queue.Peek()orfront()Acquires the data element available at the front node of the queue without deleting it.rear(): This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.isFull(): Validates if the queue is full.isNull(): Checks if the queue is empty.
Different Types of Queues¶
There are five different types of queues that are used in different scenarios.

Circular Queue¶
Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called ‘Ring Buffer’. This queue is primarily used in the following cases:
- Memory Management: The unused memory locations in the case of ordinary queues can be utilized in circular queues.
- Traffic system: In a computer-controlled traffic system, circular queues are used to switch on the traffic lights one by one repeatedly as per the time set.
- CPU Scheduling: Operating systems often maintain a queue of processes that are ready to execute or that are waiting for a particular event to occur.
Input Restricted Queue¶
In this type of Queue, the input can be taken from one side only(rear) and deletion of elements can be done from both sides(front and rear). This kind of Queue does not follow FIFO(first in first out). This queue is used in cases where the consumption of the data needs to be in FIFO order but if there is a need to remove the recently inserted data for some reason and one such case can be irrelevant data, performance issue, etc.

Output Restricted Queue¶
In this type of Queue, the input can be taken from both sides(rear and front) and the deletion of the element can be done from only one side(front). This queue is used in the case where the inputs have some priority order to be executed and the input can be placed even in the first place so that it is executed first.

Double Ended Queue (Deque)¶
Double Ended Queue is also a Queue data structure in which the insertion and deletion operations are performed at both the ends (front and rear). That means, we can insert at both front and rear positions and can delete from both front and rear positions. Since Deque supports both stack and queue operations, it can be used as both. The problems where elements need to be removed and or added both ends can be efficiently solved using Deque.

Priority Queue¶
A priority queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority and is served according to its priority. There are two types of Priority Queues. We have:
- Ascending Priority Queue: Element can be inserted arbitrarily but only smallest element can be removed. For example, suppose there is an array having elements 4, 2, 8 in the same order. So, while inserting the elements, the insertion will be in the same sequence but while deleting, the order will be 2, 4, 8.
- Descending priority Queue: Element can be inserted arbitrarily but only the largest element can be removed first from the given Queue. For example, suppose there is an array having elements 4, 2, 8 in the same order. So, while inserting the elements, the insertion will be in the same sequence but while deleting, the order will be 8, 4, 2.
Priority queue can be implemented in various ways. The time complexity corresponding to these implemetetions are in in the following table:
| Operation | peek() | insert() | delete() |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arrays | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) |
| Linked List | O(1) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Binary Heap | O(1) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Binary Search Tree | O(1) | O(log n) | O(log n) |
Applications of Queue¶
- When a resource is shared among multiple consumers. Examples include CPU scheduling, Disk Scheduling.
- When data is transferred asynchronously (data not necessarily received at the same rate as sent) between two processes. Examples include IO Buffers, pipes, etc.
- Memory management
- Traffic software ( Each light get on one by one after every time of interval of time.)