Data is a collection of a distinct small unit of information. It can be used in a variety of forms like text, numbers, media, bytes, etc. it can be stored in pieces of paper or electronic memory, etc.
Word 'Data' is originated from the word 'datum' that means 'single piece of information.' It is plural of the word datum.
The database is a collection of inter-related data which is used to retrieve, insert and delete the data efficiently. It is also used to organize the data in the form of a table, schema, views, and reports, etc.
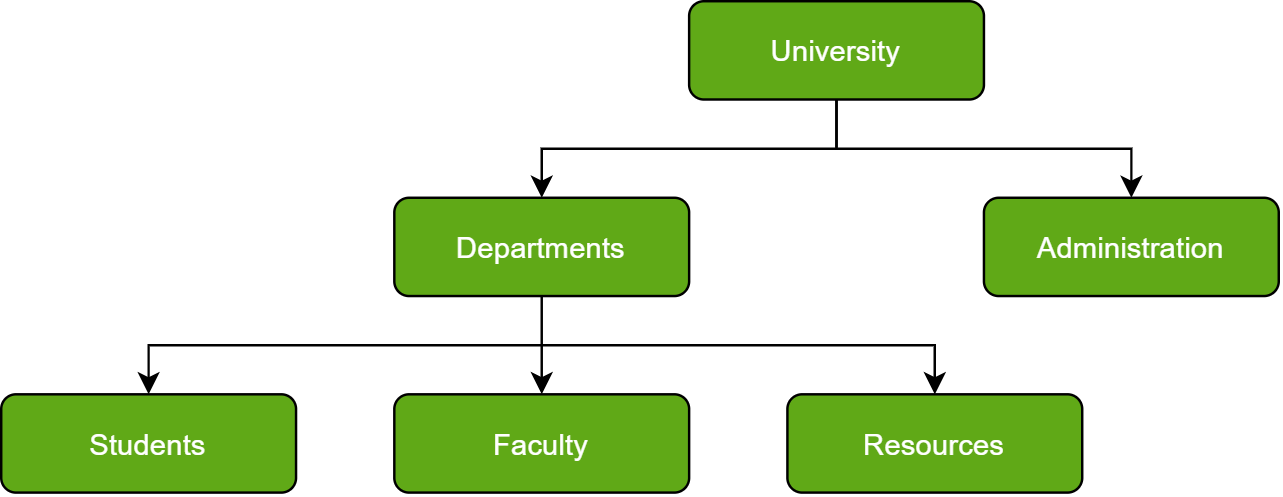
A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data are organized into a tree-like structure. The data are stored as records which are connected to one another through links. The hierarchical database model mandates that each child record has only one parent, whereas each parent record can have one or more child records. In order to retrieve data from a hierarchical database, the whole tree needs to be traversed starting from the root node. This model is recognized as the first database model created by IBM in the 1960s.

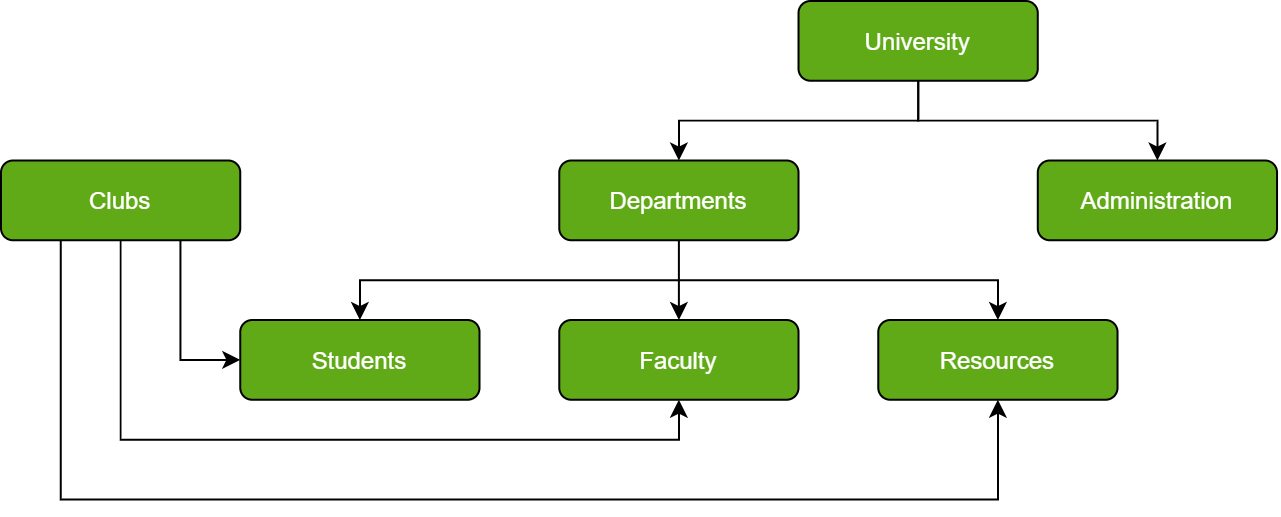
A network database is a type of database model wherein multiple member records or files can be linked to multiple owner files and vice versa. The model can be viewed as an upside-down tree where each member information is the branch linked to the owner, which is the bottom of the tree.
In Layman’s terms, a network database is a hierarchical database, but with a major tweak. The child records are given the freedom to associate with multiple parent records. As a result, a network or net of database files linked with multiple threads is observed.
An object-oriented database (OOD) is a database system that can work with complex data objects — that is, objects that mirror those used in object-oriented programming languages.
In object-oriented programming, everything is an object, and many objects are quite complex, having different properties and methods. An object-oriented database management system works in concert with an object-oriented programming language to facilitate the storage and retrieval of object-oriented data.
The elements of a OODM are:
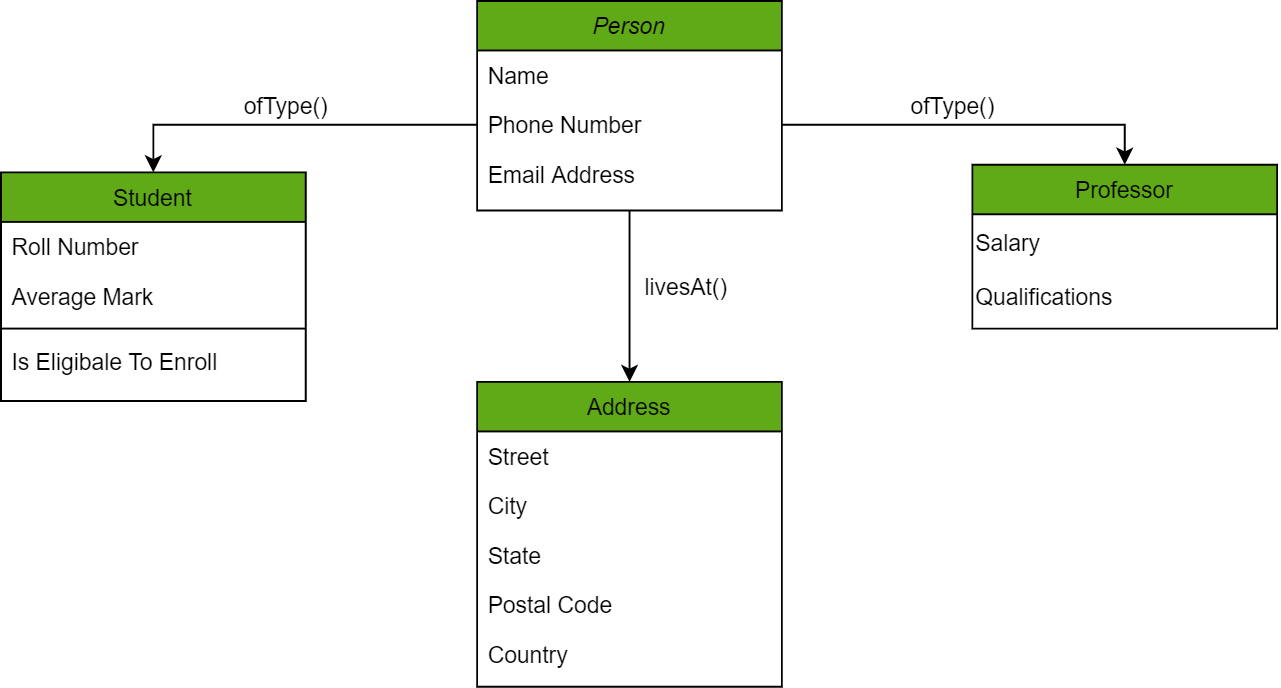
In the chart above, we have different objects linked to one another using methods; one can get the address of the Person (represented by the Person Object) using the livesAt() method. Furthermore, these objects have attributes which are in fact the data elements that need to be defined in the database.
NoSQL originally referring to non SQL or non relational is a database that provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data. This data is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases.
NoSQL systems are also sometimes called Not only SQL to emphasize the fact that they may support SQL-like query languages.
Major advantages are:
Major disadvantages are:
Types of NoSQL databases and the name of the databases system that falls in that category are:
A relational database organizes data into rows and columns, which collectively form a table. Data is typically structured across multiple tables, which can be joined together via a primary key or a foreign key. These unique identifiers demonstrate the different relationships which exist between tables, and these relationships are usually illustrated through different types of data models.
A database management system (DBMS) is system software for creating and managing databases. A DBMS makes it possible for end users to create, protect, read, update and delete data in a database. The most prevalent type of data management platform, the DBMS essentially serves as an interface between databases and users or application programs, ensuring that data is consistently organized and remains easily accessible.
Following tasks are allowed by DBMS:
The advanatges of DBMS are:
DBMS has some disadvantages too, like:
File based systems were an early attempt to computerize the manual system. It is also called a traditional based approach in which a decentralized approach was taken where each department stored and controlled its own data with the help of a data processing specialist.
Meanwhile, A database approach is a well-organized collection of data that are related in a meaningful way which can be accessed by different users but stored only once in a system. The various operations performed by the DBMS system are: Insertion, deletion, selection, sorting etc.
Some more differences are:
| Basis | DBMS Approach | File System Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | DBMS is a collection of data. In DBMS, the user is not required to write the procedures. | The file system is a collection of data. In this system, the user has to write the procedures for managing the database. |
| Sharing of data | Due to the centralized approach, data sharing is easy. | Data is distributed in many files, and it may be of different formats, so it isn't easy to share data. |
| Data Abstraction | DBMS gives an abstract view of data that hides the details. | The file system provides the detail of the data representation and storage of data. |
| Security and Protection | DBMS provides a good protection mechanism. | It isn't easy to protect a file under the file system. |
| Recovery Mechanism | DBMS provides a crash recovery mechanism, i.e., DBMS protects the user from system failure. | The file system doesn't have a crash mechanism, i.e., if the system crashes while entering some data, then the content of the file will be lost. |
| Manipulation Techniques | DBMS contains a wide variety of sophisticated techniques to store and retrieve the data. | The file system can't efficiently store and retrieve the data. |
| Concurrency Problems | DBMS takes care of Concurrent access of data using some form of locking. | In the File system, concurrent access has many problems like redirecting the file while deleting some information or updating some information. |
| Where to use | Database approach used in large systems which interrelate many files. | File system approach used in large systems which interrelate many files. |
| Cost | The database system is expensive to design. | The file system approach is cheaper to design. |
| Data Redundancy and Inconsistency | Due to the centralization of the database, the problems of data redundancy and inconsistency are controlled. | In this, the files and application programs are created by different programmers so that there exists a lot of duplication of data which may lead to inconsistency. |
| Structure | The database structure is complex to design. | The file system approach has a simple structure. |
| Data Independence | In this system, Data Independence exists, and it can be of two types.
|
In the File system approach, there exists no Data Independence. |
| Integrity Constraints | Integrity Constraints are easy to apply. | Integrity Constraints are difficult to implement in file system. |
| Data Models | In the database approach, 3 types of data models exist:
|
In the file system approach, there is no concept of data models exists. |
| Flexibility | Changes are often a necessity to the content of the data stored in any system, and these changes are more easily with a database approach. | The flexibility of the system is less as compared to the DBMS approach. |
| Examples | Oracle, SQL Server, Sybase etc. | Cobol, C++ etc. |
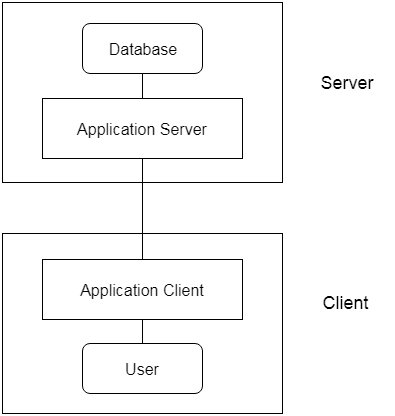
A DBMS has appropriate languages and interfaces to express database queries and updates. Database languages can be used to read, store and update the data in the database.
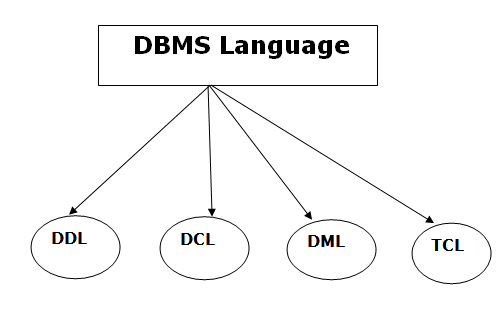
DDL is used to define database structure or pattern. It is used to create schema, tables, indexes, constraints, etc. in the database. Using the DDL statements, you can create the skeleton of the database. Data definition language is used to store the information of metadata like the number of tables and schemas, their names, indexes, columns in each table, constraints, etc.
Here are some tasks that come under DDL
It is used for accessing and manipulating data in a database. It handles user requests.
Here are some tasks that come under DML
It is used to retrieve the stored or saved data. The DCL execution is transactional. It also has rollback parameters.
Under this, we have
TCL is used to run the changes made by the DML statement. TCL can be grouped into a logical transaction.
Here,
DBMS is the management of data that should remain integrated when any changes are done in it. It is because if the integrity of the data is affected, whole data will get disturbed and corrupted. Therefore, to maintain the integrity of the data, there are four properties described in the database management system, which are known as the ACID properties.
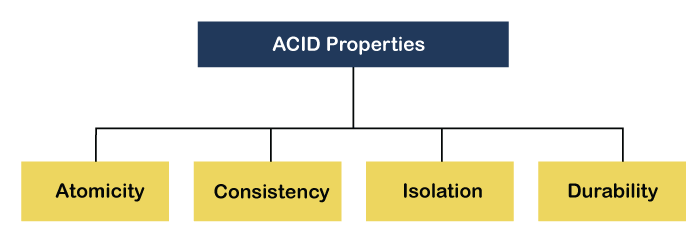
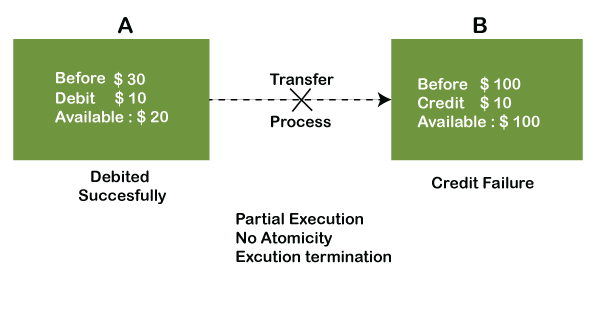
The term atomicity defines that the data remains atomic. It means if any operation is performed on the data, either it should be performed or executed completely or should not be executed at all. It further means that the operation should not break in between or execute partially. In the case of executing operations on the transaction, the operation should be completely executed and not partially.
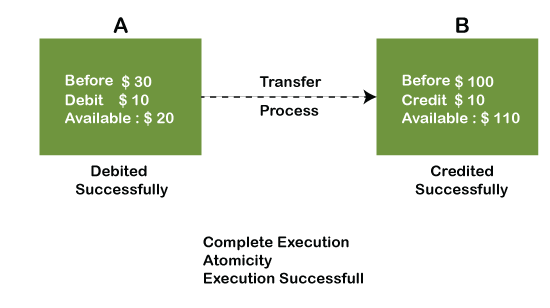
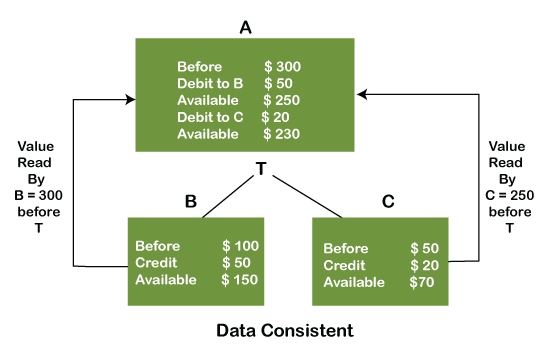
The word consistency means that the value should remain preserved always. In DBMS, the integrity of the data should be maintained, which means if a change in the database is made, it should remain preserved always. In the case of transactions, the integrity of the data is very essential so that the database remains consistent before and after the transaction.
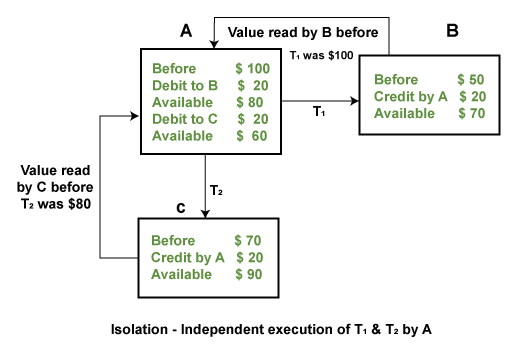
In DBMS, Isolation is the property of a database where no data should affect the other one and may occur concurrently. In short, the operation on one database should begin when the operation on the first database gets complete. It means if two operations are being performed on two different databases, they may not affect the value of one another. In the case of transactions, when two or more transactions occur simultaneously, the consistency should remain maintained. Any changes that occur in any particular transaction will not be seen by other transactions until the change is not committed in the memory.
In DBMS, the term durability ensures that the data after the successful execution of the operation becomes permanent in the database. The durability of the data should be so perfect that even if the system fails or leads to a crash, the database still survives. For committing the values, the COMMIT command must be used every time we make changes.
A transaction can be defined as a group of tasks. A single task is the minimum processing unit which cannot be divided further.
Let's talk about various states of transaction.

A transaction is said to be in a committed state if it executes all its operations successfully. In this state, all the effects are now permanently saved on the database system.
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System.
All modern database management systems like SQL, MS SQL Server, IBM DB2, ORACLE, My-SQL, and Microsoft Access are based on RDBMS. It is called Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) because it is based on the relational model. Here, data is represented in terms of tuples (rows).
Everything in a relational database is stored in the form of relations. The RDBMS database uses tables to store data. A table is a collection of related data entries and contains rows and columns to store data. Each table represents some real-world objects such as person, place, or event about which information is collected. The organized collection of data into a relational table is known as the logical view of the database.
Properties:
A row of a table is also called a record or tuple. It contains the specific information of each entry in the table. It is a horizontal entity in the table.
Properties
A column is a vertical entity in the table which contains all information associated with a specific field in a table. For example, "name" is a column in the above table which contains all information about a student's name.
Properties
The smallest unit of data in the table is the individual data item. It is stored at the intersection of tuples and attributes.
RDBMS is an extension of DBMS.
| No. | DBMS | RDBMS |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | DBMS applications store data as file. | RDBMS applications store data in a tabular form. |
| 2) | In DBMS, data is generally stored in either a hierarchical form or a navigational form. | In RDBMS, the tables have an identifier called primary key and the data values are stored in the form of tables. |
| 3) | Normalization is not present in DBMS. | Normalization is present in RDBMS. |
| 4) | DBMS does not apply any security with regards to data manipulation. | RDBMS defines the integrity constraint for the purpose of ACID (Atomocity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability) property. |
| 5) | DBMS uses file system to store data, so there will be no relation between the tables. | in RDBMS, data values are stored in the form of tables, so a relationship between these data values will be stored in the form of a table as well. |
| 6) | DBMS has to provide some uniform methods to access the stored information. | RDBMS system supports a tabular structure of the data and a relationship between them to access the stored information. |
| 7) | DBMS does not support distributed database. | RDBMS supports distributed database. |
| 8) | DBMS is meant to be for small organization and deal with small data. it supports single user. | RDBMS is designed to handle large amount of data. it supports multiple users. |
| 9) | Examples of DBMS are file systems, xml etc. | Example of RDBMS are mysql, postgre, sql server, oracle etc. |
| SQL | MySQL |
|---|---|
| SQL is Structured Query Language used to manage the relational databases. | MySQL is a relational database management system used to store, retrieve, modify and administer a database using SQL. We have a lot of database software available in the market. The popular ones include MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, Informix, etc. |
| It’s a query language. | It’s database software. It uses SQL as a language to query the database. |
| Since this is a language, it does not get updates. SQL commands always remain the same. | Since it’s a software, it gets frequent updates. |